Understanding the differences between single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer PCB
Making HDI PCB BOARD usually requires process steps such as circuit design, raw material selection, drawing, printing, gold plating and drilling. Each of these steps requires strict control and testing to ensure the quality of the pcb board manufacture.
current situation and prospects of PCB manufacturing
Our PCB products are designed to support high-speed signal transmission, allowing for faster data transfer rates and improved overall system performance.
Our PCB products incorporate advanced thermal management techniques and materials, ensuring efficient dissipation of heat and preventing overheating, which can lead to reduced performance or device failure.
PCB--An Ultimate FAQ Guide.
2.About PCB raw material procurement system
3.Do PCB products have assembly functions?
4.How much voltage can PCB products withstand?
5.Do PCB products have anti-static functions?
6.About PCB R&D capabilities
7.Does the PCB have EMC testing certification?
8.Does PCB comply with ROHS standards?
9.How much does the PCB product weigh?
10.About PCB production skills training
11.About the scale of PCB factory
12.Does the PCB have special anti-seismic design?
13.What is the temperature range of PCB products?
14.About PCB production equipment
15.About PCB raw materials
16.What is the difference between PCB FasTechCircuit vs PCB Colorful vs PCB Zotac
17.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
18.Does the PCB have a special anti-theft design?
19.How long is the service life of PCB products?
1.About PCB warranty
PCB warranty refers to the guarantee provided by manufacturers for printed circuit boards (PCBs). It ensures that the PCBs are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a specific period of time. This warranty is important as it can protect customers from potential losses caused by product defects and provides assurance of quality and reliability. Customers should pay attention to the terms and conditions of the warranty when purchasing PCBs to fully understand their rights and responsibilities in case of any issues with the product.
2.About PCB raw material procurement system
The PCB raw material procurement system is a process that involves the acquisition of necessary materials for the production of printed circuit boards. This system is essential in ensuring that the right materials are sourced in a timely and cost-effective manner to meet production demands. It involves sourcing materials from suppliers, negotiating prices, and monitoring inventory levels to maintain an efficient supply chain. A well-managed PCB raw material procurement system is crucial for maintaining the quality and efficiency of PCB production.
3.Do PCB products have assembly functions?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products do not inherently have assembly functions themselves but are designed to support the assembly of electronic components. PCBs serve as the foundational platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic parts, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors. The assembly of these components onto the PCB is a critical part of the manufacturing process of electronic devices. The design of the PCB includes features like component footprints, solder pads, and traces to facilitate the precise placement and soldering of components. While PCBs are not responsible for the assembly process, their design is tailored to enable the efficient and reliable assembly of electronic components.

4.How much voltage can PCB products withstand?
The voltage that PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can withstand varies depending on several factors, including the design, materials, and intended application. PCBs are typically designed to withstand voltages ranging from a few volts to several hundred volts. Low-power electronic devices may have PCBs that can handle lower voltages, while high-power applications, such as power distribution or industrial equipment, may require PCBs designed to withstand higher voltages. Designers consider factors like insulation, spacing, and dielectric strength when determining the voltage tolerance of a PCB to ensure safe and reliable operation within its specified limits.
5.Do PCB products have anti-static functions?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products themselves do not typically have inherent anti-static functions. However, anti-static precautions are essential during the manufacturing and handling of PCBs. Static electricity can potentially damage sensitive electronic components on a PCB. To mitigate this risk, anti-static measures such as using anti-static workstations, wearing anti-static garments, and using anti-static tools and packaging materials are employed when working with PCBs. These precautions help prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) and protect the integrity of the components and the PCB itself, ensuring that the final product functions reliably in electronic systems.
6.About PCB R&D capabilities
PCB is an integral component in electronic devices, and its development requires advanced research and development capabilities. With continuous innovation and technological advancements, PCB R&D capabilities have greatly improved. These capabilities include design and layout, material selection, prototyping, testing, and production optimization. Through rigorous research and collaboration with various industries, PCB manufacturers are able to meet the constantly evolving demands and provide efficient and reliable solutions for electronic devices.

7.Does the PCB have EMC testing certification?
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) testing certification is typically not a feature of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products themselves. Instead, EMC testing and certification are applied to the entire electronic system or device in which the PCB is used. EMC testing ensures that the electronic system complies with electromagnetic compatibility standards, meaning it can operate without causing or suffering from electromagnetic interference. While PCBs play a role in ensuring EMC compliance, the certification process involves evaluating the entire system's performance, including the PCB, components, and enclosure. Therefore, PCBs do not have EMC testing certification on their own but contribute to the overall EMC compliance of the electronic systems they are a part of.
8.Does PCB comply with ROHS standards?
Many PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturers and products aim to comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards. RoHS is a regulation that restricts the use of certain hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, in electronic and electrical equipment. Compliance with RoHS standards is crucial for environmental and safety reasons, as it helps reduce the use of harmful substances in electronics and their potential impact on health and the environment. However, RoHS compliance can vary between manufacturers and specific PCB products, so it's essential to verify compliance with the relevant regulations and standards for a particular PCB product.
9.How much does the PCB product weigh?
The weight of the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) product can vary significantly depending on its size, material, and complexity. Typically, PCBs are lightweight components in electronic devices, with smaller PCBs weighing only a few grams, while larger and more intricate PCBs may weigh several ounces or more. The weight of the PCB is influenced by factors such as the thickness of the board, the number of layers, the presence of additional components, and the type of materials used in its construction. It is essential to consider the weight of the PCB when designing electronic systems to ensure that it meets the specific requirements of the application.
10.About PCB production skills training
PCB production skills training is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process in the electronics industry. It involves providing individuals with the necessary knowledge and expertise required for the production of high-quality printed circuit boards (PCBs). This training covers various techniques and methodologies, such as design principles, fabrication processes, and assembly methods, to ensure efficient and accurate production. With a strong emphasis on practical learning, this training equips individuals with the skills needed to meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry and deliver top-notch PCBs.
11.About the scale of PCB factory
The scale of a PCB factory refers to its size and production capacity. It may vary greatly depending on the company's resources and operations. Typically, a PCB factory will have a large and well-equipped manufacturing facility, with specialized equipment and machinery to produce circuit boards in large quantities. The factory may also have a sizeable workforce, including engineers, technicians, and workers, who are trained and experienced in PCB production. The scale of the factory also plays an essential role in meeting the demands of clients and keeping up with the rapid advancements in technology. A larger and more advanced PCB factory can provide a wider range of services and offer faster production times, making them more competitive in the market. Overall, the scale of a PCB factory reflects its capabilities and success in meeting the growing demands of the electronics industry.
12.Does the PCB have special anti-seismic design?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products typically do not have special anti-seismic designs as their primary function is to provide electrical connections and support for electronic components. Anti-seismic considerations are generally addressed at the system level in applications like industrial equipment, automotive electronics, or aerospace systems, where the entire system's design may incorporate anti-seismic measures to ensure stability and functionality during mechanical stress or vibrations. While PCBs themselves are not designed for anti-seismic purposes, they are integrated into systems that may have such protection in place to prevent damage or malfunction during seismic events.
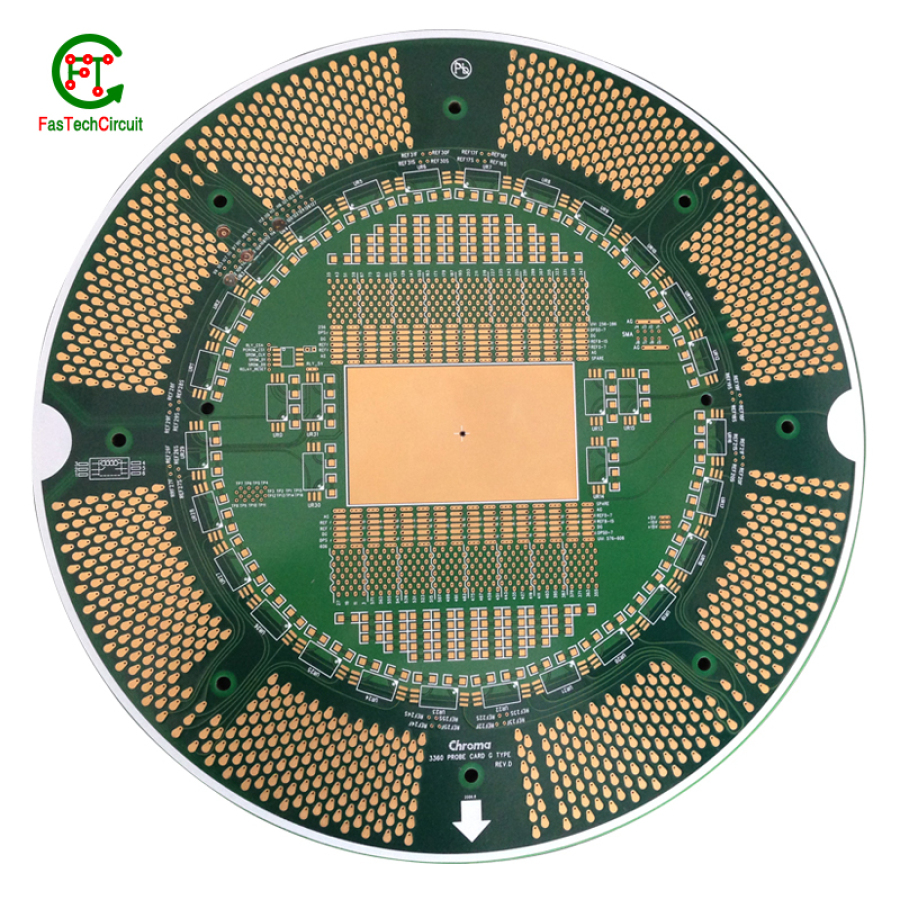
13.What is the temperature range of PCB products?
The temperature range of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can vary significantly depending on their design and the materials used. PCBs are typically specified with an operating temperature range, which indicates the temperatures at which they can safely and reliably function. Common temperature ranges for PCBs in standard electronic devices are -40°C to 85°C or 0°C to 70°C. However, for specialized applications, such as industrial or automotive electronics, PCBs may have wider operating temperature ranges, extending from -40°C to 125°C or higher. The choice of temperature range depends on the intended application and environmental conditions in which the PCB will be used, ensuring that it can withstand the required temperature extremes without degradation in performance.
14.About PCB production equipment
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) production equipment refers to a set of machinery and tools used in the manufacturing process of PCBs. These equipment include machines for etching, drilling, plating, soldering, and testing of printed circuit boards. They are crucial for automating and streamlining the production process, ensuring the efficiency and accuracy of PCB manufacturing. With the continuous advancements in technology, the PCB production equipment has also evolved, becoming more advanced and sophisticated, allowing for the production of high-quality and complex PCBs. This equipment is essential in the electronics industry, as it enables the efficient production of electronic devices that are vital to our daily lives.
15.About PCB raw materials
PCB (printed circuit board) raw materials refer to the materials used to manufacture PCBs, which serve as the backbone of electronic devices. These materials can include various types of substrates, such as fiberglass, ceramic, and plastic, as well as copper, tin, and other metals for the conductive layers and traces. Other essential components include solder masks, silkscreen printing inks, and metal finishes. The selection of these raw materials is crucial in determining the quality, durability, and performance of the final PCB product. Advances in technology have led to the development of new and improved raw materials, allowing for more compact and efficient PCB designs.

16.What is the difference between PCB FasTechCircuit vs PCB Colorful vs PCB Zotac
The choice between these manufacturers should be based on your specific project requirements. PCB FasTechCircuit is suitable for rapid prototyping, while PCB Colorful and PCB Zotac are trusted options for high-quality components in computer hardware, with a specific emphasis on gaming and graphics cards. Your decision should align with the goals and needs of your project.
17.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
The electrical characteristics of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) are vital for its performance in electronic systems. These characteristics include impedance, dielectric constant (Dk), crosstalk, signal integrity, capacitance, inductance, voltage and current handling, frequency response, and high-frequency performance. PCBs are designed to maintain controlled impedance, minimize signal interference, and handle specific voltage and current levels, ensuring their reliability and functionality in various electronic applications. The choice of materials and design considerations plays a significant role in achieving the desired electrical characteristics for PCBs.
18.Does the PCB have a special anti-theft design?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products typically do not have a special anti-theft design themselves. Anti-theft features are usually implemented at the level of the entire electronic system or device in which the PCB is incorporated. These features may include encryption, secure access control, or tamper-evident packaging to prevent unauthorized access or use of the device. While the PCB may play a role in security by facilitating secure connections or encryption features, its primary function is to provide electrical connectivity within electronic devices. Anti-theft measures are usually implemented at the system level, not at the PCB level.
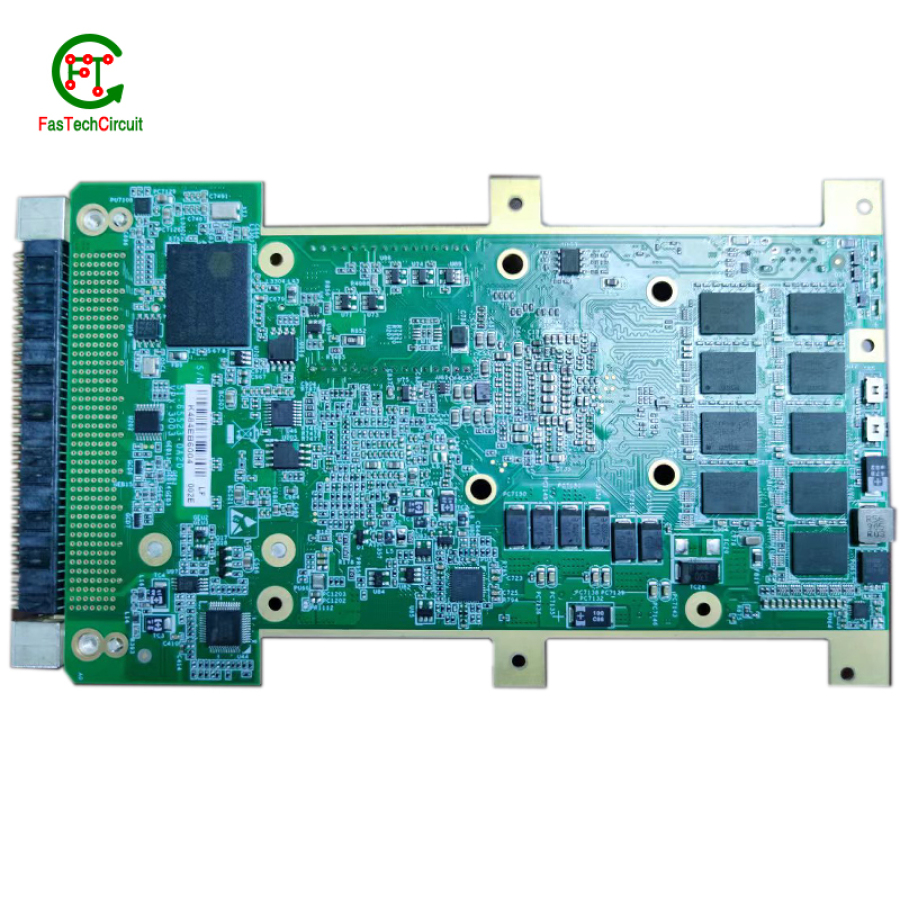
19.How long is the service life of PCB products?
The service life of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the quality of materials, manufacturing processes, and the conditions under which the PCB is used. In many cases, well-designed and properly manufactured PCBs can have a service life of several years to decades. High-quality materials and careful assembly can contribute to longer-lasting PCBs. However, environmental factors, temperature extremes, humidity, and the level of wear and tear can impact the service life. For critical applications, extended service life is essential, and durability is a key consideration in the PCB's design and manufacturing process. Regular maintenance and proper handling can also help extend the life of PCB products.
RELATED NEWS
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.






