Multilayer PCB oveerview: difinition, types, how to choose?
Multilayer PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a type of circuit board that has multiple layers of conductive material separated by insulating layers. It is used in electronic devices and equipment for connecting and supporting electronic components such as integrated circuits, resistors, and capacitors. The number of layers in a multilayer PCB can range from 4 to 30 or more, depending on the complexity of the circuit design.
Types of Multilayer PCB:
1. Rigid Multilayer PCB: This is the most commonly used type of multilayer PCB, where the layers are connected through vias (holes filled with a conductive material). It is used in applications where high reliability and durability are required.
2. Flexible Multilayer PCB: This type of multilayer PCB is made up of flexible layers of thin, flexible material such as polyimide, which allows the PCB to bend and twist without breaking. It is used in applications where space and weight are a constraint.
3. Rigid-Flex Multilayer PCB: This is a combination of rigid and flexible PCBs, where the flexible layers are interconnected to the rigid sections through vias. It is used in applications where both flexibility and durability are required.
4. High Density Interconnect (HDI) Multilayer PCB: This type of multilayer PCB has a higher number of layers and smaller via holes, which allows for a higher density of components and traces. It is used in high-speed and high-frequency applications.
How to choose a Multilayer PCB:
1. Number of Layers: The number of layers required in a multilayer PCB depends on the complexity of the circuit design and the density of components. It is important to consider the number of layers needed to ensure efficient operation of the circuit.
2. Material: The choice of material for the PCB should be based on the requirements of the application. Rigid PCBs are suitable for high reliability and durability, while flexible PCBs are preferred for applications with space and weight constraints. HDI PCBs are used in high-speed and high-frequency applications.
3. PCB Thickness: The thickness of the multilayer PCB is an important factor to consider, as it can affect the overall size and weight of the electronic device. Thinner boards are typically used in portable devices, while thicker boards are used in applications where durability is important.
4. Traces and Vias: The width of traces and the size of vias should be carefully considered to ensure proper functioning of the circuit. Smaller vias and traces are required for high-density designs, while larger ones are suitable for low-frequency applications.
5. Cost: The cost of a multilayer PCB depends on its complexity, size, and material used. It is important to consider the cost implications of the chosen PCB design and material, as it can affect the overall cost of the electronic device.
choosing the right type of multilayer PCB is crucial for the efficient operation of electronic devices. Factors such as number of layers, material, thickness, traces, and cost should be carefully considered to ensure the best possible performance.
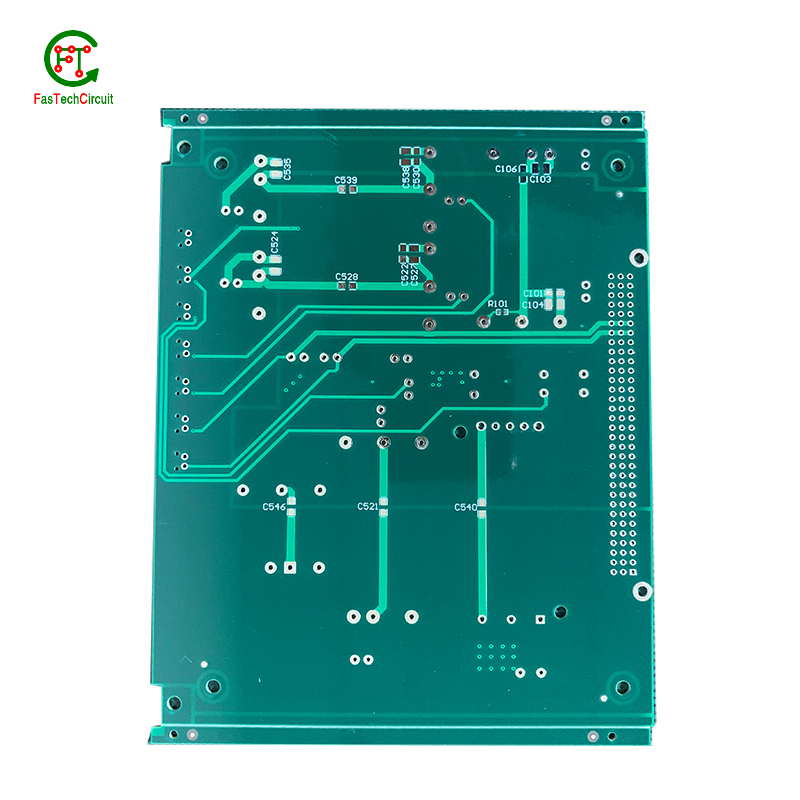
Our multilayer PCB for automotive applications is specifically designed to meet the demands of the automotive industry. With high-temperature resistance, superior mechanical strength, and excellent signal integrity, this PCB is built to withstand harsh automotive environments. Its multilayer design allows for increased functionality and performance, making it the perfect choice for modern automotive electronics such as advanced driver assistance systems, infotainment systems, and more.
2.Can multilayer PCBs support high-power applications?
3.Are multilayer PCBs more expensive than single-sided PCBs?
4.How do I choose the right thickness for my multilayer PCB?
5.What is the difference between a multilayer and a flex PCB?
6.Can multilayer PCBs be used for high-frequency applications?
1.What materials are used to make multilayer PCBs?
Multilayer PCBs are typically made from layers of copper, epoxy resin, and glass fiber. Other materials such as polyimide and ceramic may also be used for specific applications.
2.Can multilayer PCBs support high-power applications?
Yes, multilayer PCBs can support high-power applications with the use of thicker copper layers and appropriate thermal management techniques.
3.Are multilayer PCBs more expensive than single-sided PCBs?
Yes, multilayer PCBs are generally more expensive than single-sided PCBs due to the complexity and additional layers involved in their manufacturing.
4.How do I choose the right thickness for my multilayer PCB?
The thickness of a multilayer PCB is determined by the design requirements and the capabilities of the manufacturer. It is best to consult with a PCB manufacturer to determine the appropriate thickness for your application.
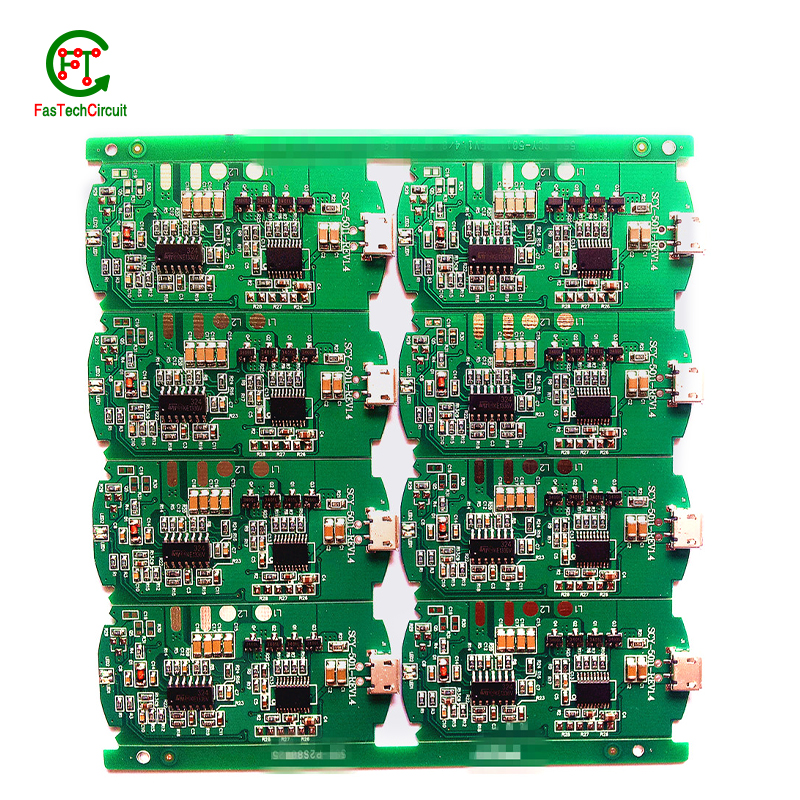
5.What is the difference between a multilayer and a flex PCB?
A multilayer PCB is rigid and does not allow bending, while a flex PCB is made of flexible materials and allows for bending and twisting. Both types can have multiple conductive layers.
6.Can multilayer PCBs be used for high-frequency applications?
Yes, multilayer PCBs are suitable for high-frequency applications due to their reduced signal loss and improved signal integrity.
RELATED NEWS
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.






