The importance of controlled impedance in high-speed PCB
Making keyboard pcb usually requires process steps such as circuit design, raw material selection, drawing, printing, gold plating and drilling. Each of these steps requires strict control and testing to ensure the quality of the pcb manufacturing.
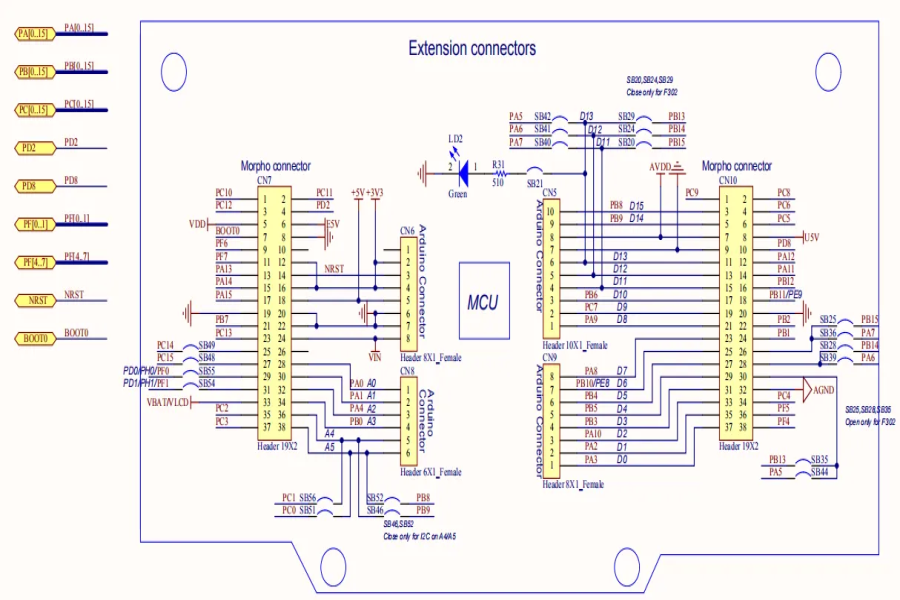
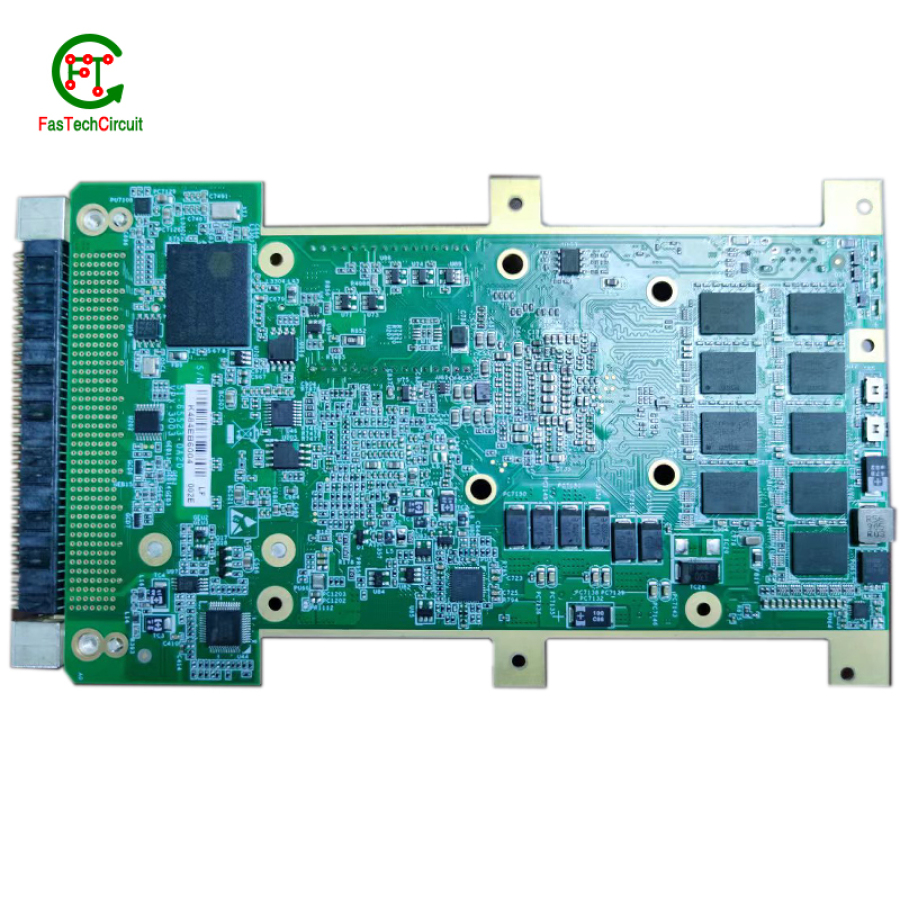
Optimizing PCB layout: the key to improving circuit performance
We are committed to using environmentally friendly materials and production processes in the manufacturing of our PCB products, reducing our carbon footprint and promoting sustainability.
The PCB materials and trace routing used in our products are carefully selected and optimized to maintain low impedance, providing efficient signal transmission and minimizing electromagnetic interference.
PCB--An Ultimate FAQ Guide.
2.About PCB warranty
3.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
4.Does the PCB have a special anti-theft design?
5.Does the PCB product have the function of preventing short circuit?
6.About PCB production equipment
7.About the development history of PCB factory
8.About PCB raw material procurement system
9.What is the surface treatment of PCB?
10.What electronic components can this PCB product support?
11.What is the difference between PCB FasTechCircuit vs PCB Biostar vs PCB EVGA
12.How many layers of circuits does a PCB product have?
13.Do PCB products have anti-static functions?
14.Does PCB have the ability to resist electromagnetic interference?
15.What is the temperature range of PCB products?
16.What is the processing accuracy of PCB products?
17.Does the PCB have EMC testing certification?
18.About the scale of PCB factory
19.About PCB origin
20.About PCB production capacity
1.How long is the service life of PCB products?
The service life of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the quality of materials, manufacturing processes, and the conditions under which the PCB is used. In many cases, well-designed and properly manufactured PCBs can have a service life of several years to decades. High-quality materials and careful assembly can contribute to longer-lasting PCBs. However, environmental factors, temperature extremes, humidity, and the level of wear and tear can impact the service life. For critical applications, extended service life is essential, and durability is a key consideration in the PCB's design and manufacturing process. Regular maintenance and proper handling can also help extend the life of PCB products.
2.About PCB warranty
PCB warranty refers to the guarantee provided by manufacturers for printed circuit boards (PCBs). It ensures that the PCBs are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a specific period of time. This warranty is important as it can protect customers from potential losses caused by product defects and provides assurance of quality and reliability. Customers should pay attention to the terms and conditions of the warranty when purchasing PCBs to fully understand their rights and responsibilities in case of any issues with the product.
3.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
The electrical characteristics of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) are vital for its performance in electronic systems. These characteristics include impedance, dielectric constant (Dk), crosstalk, signal integrity, capacitance, inductance, voltage and current handling, frequency response, and high-frequency performance. PCBs are designed to maintain controlled impedance, minimize signal interference, and handle specific voltage and current levels, ensuring their reliability and functionality in various electronic applications. The choice of materials and design considerations plays a significant role in achieving the desired electrical characteristics for PCBs.
4.Does the PCB have a special anti-theft design?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products typically do not have a special anti-theft design themselves. Anti-theft features are usually implemented at the level of the entire electronic system or device in which the PCB is incorporated. These features may include encryption, secure access control, or tamper-evident packaging to prevent unauthorized access or use of the device. While the PCB may play a role in security by facilitating secure connections or encryption features, its primary function is to provide electrical connectivity within electronic devices. Anti-theft measures are usually implemented at the system level, not at the PCB level.
5.Does the PCB product have the function of preventing short circuit?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products are designed with features and measures to prevent short circuits. These measures include the careful routing of traces to avoid unintentional connections, the use of insulating materials to separate conductive layers, and the application of solder masks to protect copper traces. Additionally, the design and manufacturing processes of PCBs aim to minimize the risk of short circuits. However, the effectiveness of short-circuit prevention depends on the quality of design, manufacturing, and adherence to best practices. PCBs are an essential component in ensuring that electrical connections are made safely and reliably without causing short circuits in electronic systems.

6.About PCB production equipment
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) production equipment refers to a set of machinery and tools used in the manufacturing process of PCBs. These equipment include machines for etching, drilling, plating, soldering, and testing of printed circuit boards. They are crucial for automating and streamlining the production process, ensuring the efficiency and accuracy of PCB manufacturing. With the continuous advancements in technology, the PCB production equipment has also evolved, becoming more advanced and sophisticated, allowing for the production of high-quality and complex PCBs. This equipment is essential in the electronics industry, as it enables the efficient production of electronic devices that are vital to our daily lives.
7.About the development history of PCB factory
The development of PCB factories can be traced back to the early 20th century when the technology for producing printed circuit boards was first invented. Over the years, with the advancements in electronics and manufacturing processes, the demand for PCBs grew rapidly. This led to the establishment of more specialized and efficient PCB factories, which played a crucial role in the development of modern electronics. With the introduction of more sophisticated machinery and techniques, these factories were able to mass produce high-quality PCBs at a faster pace, meeting the growing demand from various industries. Today, PCB factories continue to evolve and innovate, adopting new technologies such as automation and AI to streamline processes and produce higher quality and more complex circuit boards for the ever-expanding electronics market.
8.About PCB raw material procurement system
The PCB raw material procurement system is a crucial aspect of the production process for printed circuit boards. It involves the sourcing and acquisition of all necessary materials, such as copper foil, laminate sheets, solder mask, and components, needed for the manufacturing of PCBs. This system requires efficient coordination between suppliers and the PCB manufacturer to ensure timely delivery and high-quality materials. Additionally, proper management of inventory levels and cost control are essential components of the procurement system to ensure smooth and cost-effective production of PCBs.
9.What is the surface treatment of PCB?
Common surface treatment methods include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives), and immersion tin or silver. The choice of treatment method depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and its intended application.
10.What electronic components can this PCB product support?
The capabilities of this PCB (Printed Circuit Board) product extend to supporting a wide array of electronic components. These components include but are not limited to integrated circuits (ICs), microcontrollers, resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, connectors, and various sensors. The PCB's design and layout are tailored to accommodate these components and establish electrical connections between them. This versatility enables the PCB to be used in a broad spectrum of electronic devices and systems, where it acts as the central hub for component integration and electrical functionality.
11.What is the difference between PCB FasTechCircuit vs PCB Biostar vs PCB EVGA
The choice between these manufacturers should be based on your specific project requirements. PCB FasTechCircuit is ideal for fast prototyping, while PCB Biostar and PCB EVGA are trusted options for high-quality components in computer hardware, with EVGA specifically known for its gaming-oriented graphics cards. Your decision should align with the goals and needs of your project.
12.How many layers of circuits does a PCB product have?
The number of layers in a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) product can vary widely and is determined by the complexity of the electronic circuit it serves. PCBs can have a single layer (single-sided), two layers (double-sided), or multiple layers, often referred to as multilayer PCBs. Multilayer PCBs can have three or more layers, with some advanced designs featuring more than 20 layers. The choice of the number of layers depends on the specific requirements of the electronic system, including the complexity of the circuit, the need for signal integrity, and space constraints. Multilayer PCBs are commonly used in complex electronic devices, such as smartphones, computers, and industrial equipment, where they provide the necessary space for intricate circuits and connections.
13.Do PCB products have anti-static functions?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products themselves do not typically have inherent anti-static functions. However, anti-static precautions are essential during the manufacturing and handling of PCBs. Static electricity can potentially damage sensitive electronic components on a PCB. To mitigate this risk, anti-static measures such as using anti-static workstations, wearing anti-static garments, and using anti-static tools and packaging materials are employed when working with PCBs. These precautions help prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) and protect the integrity of the components and the PCB itself, ensuring that the final product functions reliably in electronic systems.
14.Does PCB have the ability to resist electromagnetic interference?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can be designed to resist electromagnetic interference (EMI) through various methods and features. EMI shielding, grounded planes, and controlled impedance routing are some common techniques used to mitigate the impact of EMI. PCB design and layout play a crucial role in minimizing EMI susceptibility and emissions. Additionally, the selection of materials and components can influence the PCB's EMI resistance. Proper grounding, signal isolation, and use of EMI shielding materials can help ensure that PCBs perform well in EMI-prone environments. The level of EMI resistance depends on the design and materials used, making it an important consideration in applications where EMI can affect electronic performance.
15.What is the temperature range of PCB products?
The temperature range of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can vary significantly depending on their design and the materials used. PCBs are typically specified with an operating temperature range, which indicates the temperatures at which they can safely and reliably function. Common temperature ranges for PCBs in standard electronic devices are -40°C to 85°C or 0°C to 70°C. However, for specialized applications, such as industrial or automotive electronics, PCBs may have wider operating temperature ranges, extending from -40°C to 125°C or higher. The choice of temperature range depends on the intended application and environmental conditions in which the PCB will be used, ensuring that it can withstand the required temperature extremes without degradation in performance.

16.What is the processing accuracy of PCB products?
The processing accuracy of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products is a critical aspect of their quality. It involves ensuring that the dimensions, traces, holes, and other features of the PCB are fabricated with precision. The accuracy is typically specified in terms of tolerances for various parameters, including trace width, hole diameter, and overall dimensions. Common processing accuracy standards for PCBs include a minimum trace width and spacing, as well as specific tolerances for holes and cutouts. Achieving high processing accuracy is essential to ensure that the PCB functions as intended and that components can be soldered onto it without issues. The specific processing accuracy requirements can vary based on the PCB's design and application.
17.Does the PCB have EMC testing certification?
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) testing certification is typically not a feature of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products themselves. Instead, EMC testing and certification are applied to the entire electronic system or device in which the PCB is used. EMC testing ensures that the electronic system complies with electromagnetic compatibility standards, meaning it can operate without causing or suffering from electromagnetic interference. While PCBs play a role in ensuring EMC compliance, the certification process involves evaluating the entire system's performance, including the PCB, components, and enclosure. Therefore, PCBs do not have EMC testing certification on their own but contribute to the overall EMC compliance of the electronic systems they are a part of.
18.About the scale of PCB factory
The scale of a PCB factory refers to its size and production capacity. It may vary greatly depending on the company's resources and operations. Typically, a PCB factory will have a large and well-equipped manufacturing facility, with specialized equipment and machinery to produce circuit boards in large quantities. The factory may also have a sizeable workforce, including engineers, technicians, and workers, who are trained and experienced in PCB production. The scale of the factory also plays an essential role in meeting the demands of clients and keeping up with the rapid advancements in technology. A larger and more advanced PCB factory can provide a wider range of services and offer faster production times, making them more competitive in the market. Overall, the scale of a PCB factory reflects its capabilities and success in meeting the growing demands of the electronics industry.
19.About PCB origin
PCB, short for Printed Circuit Board, is one of the essential components in electronic devices. It serves as a foundation and support for electronic components, allowing them to be connected and work together. The origin of PCB can be traced back to the early 20th century when people found a need to create a more efficient and reliable way to connect, mount, and organize electronic components. Over time, with the development of technology and manufacturing processes, PCB has become an integral part of modern electronic devices, making our daily lives more convenient and connected. Today, PCBs are widely used in various industries, from consumer electronics to medical equipment, highlighting their critical role and contribution to the advancement of technology.
20.About PCB production capacity
PCB production capacity refers to the amount and ability of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturer to produce electronic circuit boards in a given period of time. This includes the company's production capabilities, resources, and efficiency in producing PCBs. The capacity of a PCB manufacturer is an important consideration for businesses and industries that rely on PCBs for their electronic devices, as it directly impacts the supply and turnaround time for these crucial components. With the constant demand for smaller, faster, and more complex electronic devices, there is a growing need for PCB production capacity to keep up with the industry's evolving requirements. Therefore, manufacturers are continuously investing in technology and expanding their production capabilities to meet the demands of the market.
TAG: PCB, PCBA, HIGH SPEED PCB
RELATED NEWS
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.






