The role and importance of vias in PCB design
custom pcb is widely used in electronic products, such as computers, mobile phones, TVs, stereos, etc. Almost all electronic devices are inseparable from PCB technology.
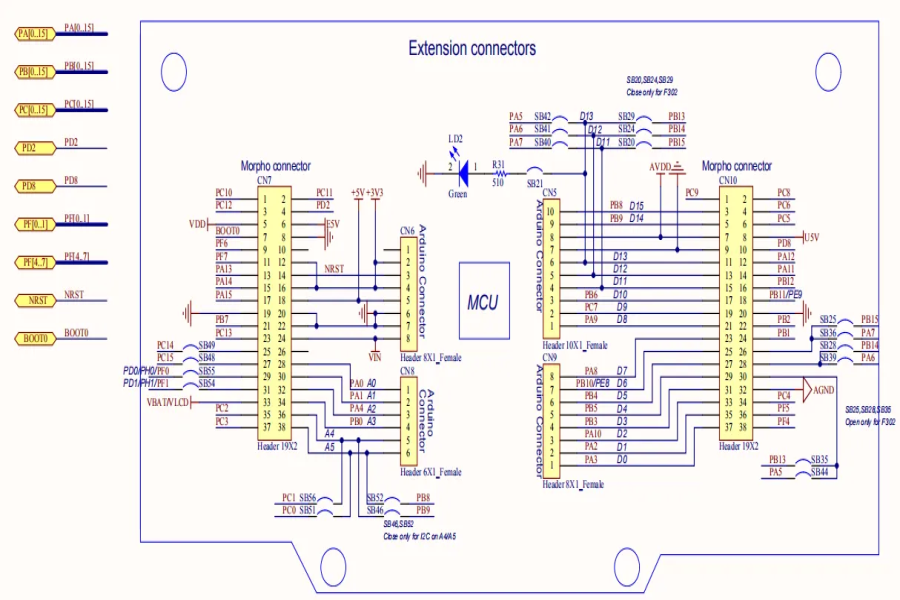
current situation and prospects of PCB manufacturing
Our PCB products are designed to support high-speed signal transmission, allowing for faster data transfer rates and improved overall system performance.
Our PCB products incorporate advanced thermal management techniques and materials, ensuring efficient dissipation of heat and preventing overheating, which can lead to reduced performance or device failure.
PCB--An Ultimate FAQ Guide.
2.Does PCB have fire protection function?
3.Are PCB products waterproof?
4.About PCB MOQ
5.About PCB technology
6.Does the PCB have special anti-seismic design?
7.What kind of production process is used for PCB products?
8.What is the operating temperature of PCB?
9.Do PCB products have assembly functions?
10.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
11.What is the surface treatment of PCB?
12.About PCB patent
13.About PCB production capacity
14.About PCB production management system
15.About PCB production equipment
16.About PCB quality system
17.About PCB inventory
18.How is the circuit layout of PCB products designed?
19.About the scale of PCB factory
20.What electronic fields is PCB suitable for?
21.About PCB customization services
22.What kind of connection methods does the PCB product support?
23.Does the PCB have high voltage isolation function?
1.About PCB production skills training
PCB production skills training is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process in the electronics industry. It involves providing individuals with the necessary knowledge and expertise required for the production of high-quality printed circuit boards (PCBs). This training covers various techniques and methodologies, such as design principles, fabrication processes, and assembly methods, to ensure efficient and accurate production. With a strong emphasis on practical learning, this training equips individuals with the skills needed to meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry and deliver top-notch PCBs.
2.Does PCB have fire protection function?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products typically do not have inherent fire protection functions, as they are primarily designed for electrical connections and circuitry. However, the fire resistance of a PCB can be influenced by the materials used in its construction. For example, some PCB materials may have fire-resistant properties and can inhibit the spread of flames when exposed to high temperatures. In applications where fire resistance is crucial, such as aerospace or critical industrial systems, special PCB materials with fire-resistant properties may be chosen to enhance safety. Fire protection, in such cases, is typically a consideration beyond the PCB itself, involving the overall design and materials used in the electronic system.
3.Are PCB products waterproof?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products are not inherently waterproof, but they can be made water-resistant or waterproof by applying specific protective measures during the design and manufacturing process. Water-resistant PCBs are often coated with conformal coatings or encapsulated in waterproof housings to shield them from moisture and environmental factors. The degree of waterproofing can vary, with some PCBs designed to withstand exposure to water and others being more water-resistant. The level of protection depends on the intended application and the environmental conditions in which the PCB will operate. Waterproofing is crucial for applications where PCBs may be exposed to moisture, such as in outdoor electronics, automotive systems, and marine devices.
4.About PCB MOQ
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for printed circuit boards (PCBs) refers to the minimum number of boards that must be purchased in a single order. It is typically set by PCB manufacturers to ensure cost effectiveness and efficiency in production. The MOQ may vary depending on factors such as board size, layers, materials, and technology. It is important for companies or individuals to understand the MOQ before placing an order to avoid unnecessary costs and delays in production.

5.About PCB technology
PCB technology, also known as Printed Circuit Board technology, is a fundamental aspect of modern electronics. It involves designing and manufacturing electronic circuits and interconnecting components using conductive pathways, or traces, on a non-conductive substrate. This technology has revolutionized the electronic industry and has enabled the creation of highly efficient and compact electronic devices, from smartphones to computers and medical equipment. PCB technology continues to advance with the demand for smaller, faster, and more complex electronic devices, making it a crucial component in the development of new technologies.
6.Does the PCB have special anti-seismic design?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products typically do not have special anti-seismic designs as their primary function is to provide electrical connections and support for electronic components. Anti-seismic considerations are generally addressed at the system level in applications like industrial equipment, automotive electronics, or aerospace systems, where the entire system's design may incorporate anti-seismic measures to ensure stability and functionality during mechanical stress or vibrations. While PCBs themselves are not designed for anti-seismic purposes, they are integrated into systems that may have such protection in place to prevent damage or malfunction during seismic events.
7.What kind of production process is used for PCB products?
The production process for PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products involves several key stages. It begins with design, where engineers plan the layout of electrical connections and component placement using specialized software. Material selection is a crucial step, followed by etching to remove unwanted copper, drilling for component holes, and plating to create plated-through holes. Solder mask application protects copper traces, and silkscreen printing provides component labels. Testing and quality control ensure functionality and adherence to standards, and the final step is component assembly, where electronic parts are soldered onto the PCB. The specific details of each stage may vary based on the PCB's complexity and the manufacturing processes employed.
8.What is the operating temperature of PCB?
The operating temperature of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) can vary depending on its design, materials, and intended application. PCBs are typically specified with an operating temperature range that indicates the temperatures at which they can safely and reliably function. Common temperature ranges for standard PCBs in electronic devices are -40°C to 85°C or 0°C to 70°C. However, for specialized applications, such as industrial or automotive electronics, PCBs may have wider operating temperature ranges, extending from -40°C to 125°C or higher. The choice of temperature range depends on the intended application and environmental conditions in which the PCB will be used, ensuring that it can withstand the required temperature extremes without degradation in performance.
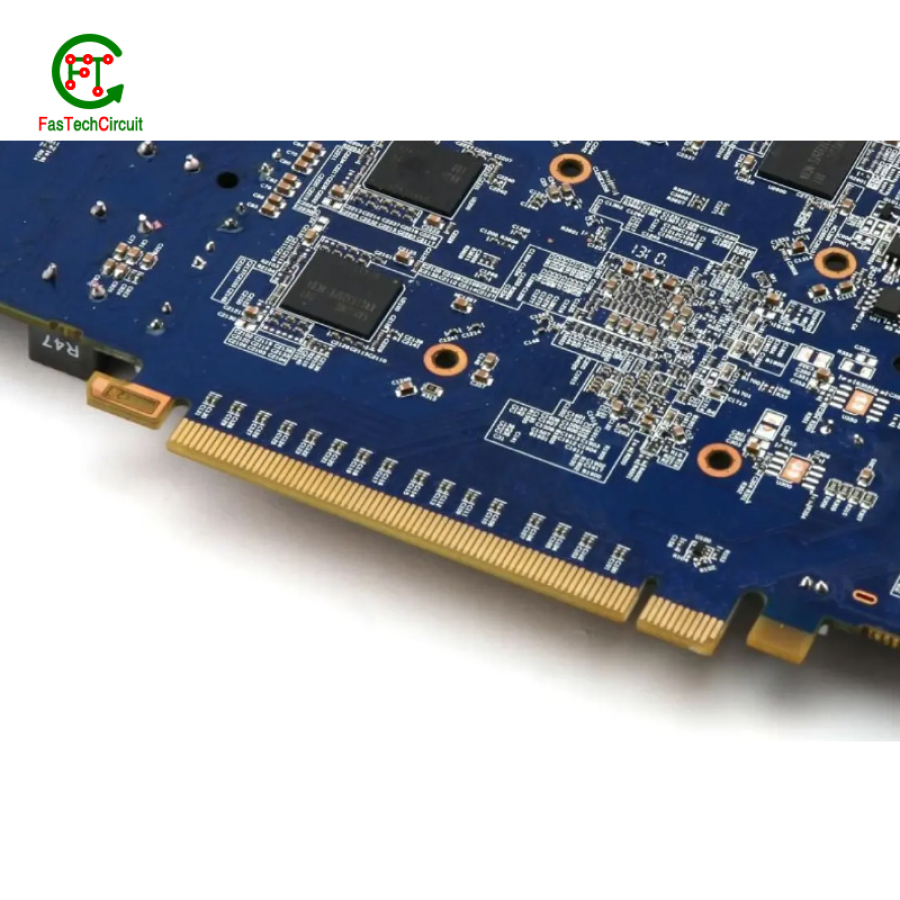

9.Do PCB products have assembly functions?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products do not inherently have assembly functions themselves but are designed to support the assembly of electronic components. PCBs serve as the foundational platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic parts, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors. The assembly of these components onto the PCB is a critical part of the manufacturing process of electronic devices. The design of the PCB includes features like component footprints, solder pads, and traces to facilitate the precise placement and soldering of components. While PCBs are not responsible for the assembly process, their design is tailored to enable the efficient and reliable assembly of electronic components.
10.What are the electrical characteristics of PCB?
The electrical characteristics of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) are vital for its performance in electronic systems. These characteristics include impedance, dielectric constant (Dk), crosstalk, signal integrity, capacitance, inductance, voltage and current handling, frequency response, and high-frequency performance. PCBs are designed to maintain controlled impedance, minimize signal interference, and handle specific voltage and current levels, ensuring their reliability and functionality in various electronic applications. The choice of materials and design considerations plays a significant role in achieving the desired electrical characteristics for PCBs.
11.What is the surface treatment of PCB?
Common surface treatment methods include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives), and immersion tin or silver. The choice of treatment method depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and its intended application.
12.About PCB patent
PCB patent refers to the legal protection granted to the design, technology, or invention related to printed circuit boards (PCBs). These patents not only protect the intellectual property of PCB manufacturers and designers, but also encourage innovation and development in the electronic industry. With the increasing demand for smaller and more advanced devices, PCB patents play a crucial role in safeguarding the rights of inventors and promoting the growth of the PCB market. However, obtaining a PCB patent can be a complex and lengthy process, involving multiple legal requirements and thorough examination. The enforcement of PCB patents also requires strict adherence to patent laws and regulations to protect against infringements. Overall, PCB patents are essential for fostering innovation and ensuring fair competition in the ever-evolving world of technology.
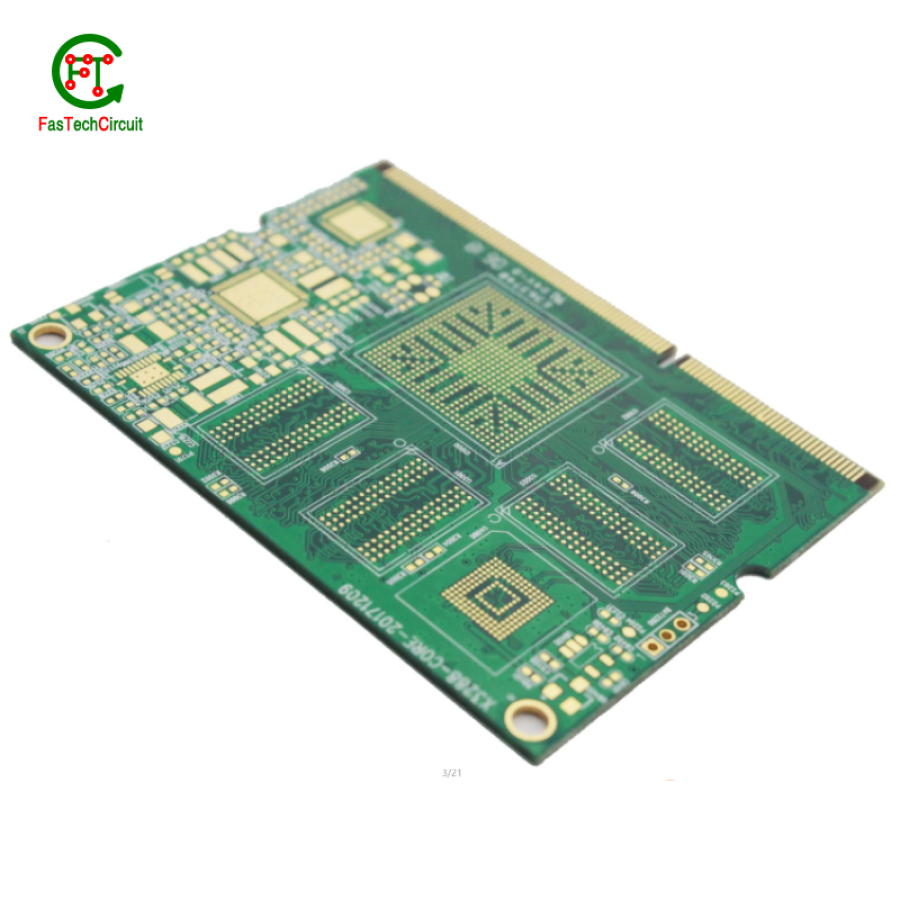

13.About PCB production capacity
PCB production capacity refers to the amount and ability of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturer to produce electronic circuit boards in a given period of time. This includes the company's production capabilities, resources, and efficiency in producing PCBs. The capacity of a PCB manufacturer is an important consideration for businesses and industries that rely on PCBs for their electronic devices, as it directly impacts the supply and turnaround time for these crucial components. With the constant demand for smaller, faster, and more complex electronic devices, there is a growing need for PCB production capacity to keep up with the industry's evolving requirements. Therefore, manufacturers are continuously investing in technology and expanding their production capabilities to meet the demands of the market.
14.About PCB production management system
The PCB production management system is a software program designed to effectively manage the entire process of producing printed circuit boards. It utilizes advanced technology to streamline and automate various tasks involved, such as order management, design and layout, material procurement, production scheduling, quality control, and shipping. This system aims to improve efficiency, reduce production time and costs, increase accuracy and quality, and provide real-time tracking and monitoring of the production process. With its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface, the PCB production management system is an essential tool for optimizing the production of printed circuit boards.
15.About PCB production equipment
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) production equipment is an essential component in the manufacturing process of electronic devices. It includes various machines and tools used to fabricate, assemble, and test printed circuit boards, which are the foundation of all electronic devices. These equipment typically include drills, routers, plating machines, soldering machines, inspection systems, and more. With the advancement of technology, PCB production equipment has become more sophisticated and efficient, allowing for higher precision and faster production times. As electronic devices continue to evolve and become more intricate, the demand for advanced PCB production equipment will only continue to grow.
16.About PCB quality system
The PCB quality system is a comprehensive and structured approach to ensuring the quality of printed circuit boards. It encompasses various processes and procedures, from design and manufacturing to testing and inspection, to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and specifications. By implementing a robust quality system, manufacturers can achieve consistent and reliable quality, reduce defects and errors, and ultimately deliver high-quality PCBs that meet the expectations of their customers. This system is crucial in the electronics industry, as PCBs are integral components in most electronic devices and their quality can greatly impact the performance and reliability of these devices.

17.About PCB inventory
PCB inventory, or printed circuit board inventory, refers to the collection of all available PCBs (printed circuit boards) in stock for a particular company or organization. These PCBs are crucial components in the production of electronic devices and serve as the foundation for the electrical connections between various components. Maintaining an efficient and well-managed PCB inventory is essential for companies to meet the demand for their products, reduce production costs, and stay competitive in the market. Regular inventory checks, tracking of usage, and proper storage and handling of PCBs are key factors in managing a successful PCB inventory.
18.How is the circuit layout of PCB products designed?
The design of the circuit layout for PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products is a meticulous process that involves the placement and interconnection of electronic components to create a functional circuit. Designers use specialized software to arrange components on the board, optimize signal flow, and ensure efficient use of space. Factors like component placement, signal traces, power distribution, and signal integrity are considered during the design process. The goal is to create an organized and efficient layout that minimizes signal interference, maximizes functionality, and meets the specific requirements of the electronic system. The final circuit layout is a critical aspect of PCB design, ensuring the reliable performance of the electronic device or system.
19.About the scale of PCB factory
The scale of a PCB factory refers to its size and production capacity. It may vary greatly depending on the company's resources and operations. Typically, a PCB factory will have a large and well-equipped manufacturing facility, with specialized equipment and machinery to produce circuit boards in large quantities. The factory may also have a sizeable workforce, including engineers, technicians, and workers, who are trained and experienced in PCB production. The scale of the factory also plays an essential role in meeting the demands of clients and keeping up with the rapid advancements in technology. A larger and more advanced PCB factory can provide a wider range of services and offer faster production times, making them more competitive in the market. Overall, the scale of a PCB factory reflects its capabilities and success in meeting the growing demands of the electronics industry.
20.What electronic fields is PCB suitable for?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) technology is versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic fields and applications. PCBs are commonly used in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, medical devices, telecommunications, IoT, renewable energy, robotics, and consumer appliances. Their ability to provide reliable and efficient connections for electronic components makes PCBs an essential element in various electronic systems, enabling innovation and functionality in diverse fields.
21.About PCB customization services
PCB customization services refer to the process of designing and producing customized printed circuit boards according to the specific needs and requirements of a customer. This service allows for the creation of unique and tailored PCBs that can meet the exact specifications of a project or product. Through collaboration with PCB manufacturers, customers can customize various aspects such as size, shape, number of layers, materials, and layout to achieve the desired functionality and performance. These services are essential for industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical devices that require specialized PCBs for their products. With PCB customization services, companies can ensure high-quality and efficient production of their electronic devices.
22.What kind of connection methods does the PCB product support?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products support a variety of connection methods to establish electrical connections between components and external devices. These connection methods include soldering, surface-mount technology (SMT), through-hole technology (THT), and various types of connectors. Soldering is a common method where components are attached to the PCB using solder joints. SMT components are mounted directly on the PCB's surface, while THT components have leads inserted through holes in the PCB and soldered on the other side. Connectors, such as USB, HDMI, or header pins, provide external interfaces for connecting to other devices or components. The choice of connection method depends on the specific requirements of the PCB's design and the intended application, ensuring flexibility in accommodating various electronic connections.
23.Does the PCB have high voltage isolation function?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products can be designed to incorporate high voltage isolation functions, particularly in applications where it's critical to prevent electrical interference or safety hazards. High voltage isolation is typically achieved through the use of isolation components like optocouplers, transformers, or capacitors, which physically separate high voltage and low voltage components on the PCB. The specific design and presence of high voltage isolation features depend on the requirements of the electronic system and the safety standards to which it must adhere. PCBs themselves may not inherently have high voltage isolation functions but can be an integral part of systems that incorporate such isolation for safety and performance reasons.
RELATED NEWS
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.






