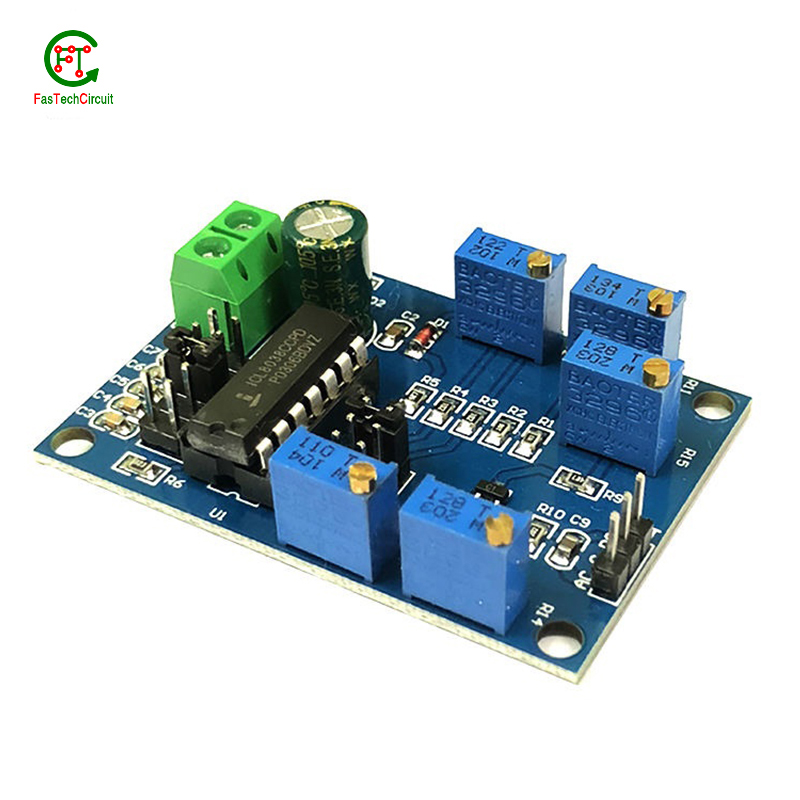
Fan Air Cooler DC Motor Control Electric Rigid Circuit Board PCB Factory China
Layer counts: 8L
Board thickness:1.6mm
Panel size: 183.14 X 98.56mm
Laminates: FR4 TG150
hole size: 0.20mm
Line width/space: 0.1/0.1mm
Surface finish: ENIG
Features: small BGA,
Application field: Fan Air Cooler DC Motor Control
WHY CHOOSE FASTECHCIRCUIT PCB?
Quick-Turn Production
FasTechCircuit offers small volume production in 5-6 days and medium-to-large production in 2 weeks.
Make Logistics Easier
When you work with FasTechCircuit , there is no need to deal with multiple suppliers, language barriers, customs headaches and shipping logistics.
We do it all - and deliver to your designated port.
Cost Savings
With our global buying power combined with the capabilities of our overseas manufacturers, we're able to provide tremendous savings for our customers.
What are the common application areas of PCBA?
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is widely used in various industries. Common application areas include consumer electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles; automotive electronics, for engine control units and infotainment systems; industrial equipment for automation and control systems; medical devices, including diagnostic equipment and patient monitoring devices; aerospace and defense for avionics and communication systems; and telecommunications infrastructure for routers, switches, and network equipment. PCBA is a fundamental technology that underpins the functioning of many electronic devices and systems across a diverse range of industries.
What should we pay attention to during PCBA production?
During PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) production, several key considerations are crucial. First, component placement accuracy and soldering quality must be closely monitored to ensure proper electrical connections. Temperature control during soldering is essential to prevent overheating or cold solder joints. Additionally, proper handling and ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection are vital to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components. Thorough testing and quality control processes, including functional testing and inspection, should be integrated to identify and rectify defects early in the production cycle. Lastly, maintaining a clean and controlled manufacturing environment is essential to prevent contamination or foreign debris from affecting the PCB assembly. These practices are critical for producing reliable and high-quality electronic assemblies.
What are the main components of PCBA?
The main components of a PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) typically include active components like microprocessors, microcontrollers, and integrated circuits, as well as passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Other important elements are connectors, switches, and LEDs for user interface and connectivity. Additionally, the PCB itself, solder, and solder paste are essential components that facilitate the electrical connections and mechanical support of the assembly. These components work together to create functional electronic circuits on a printed circuit board.
How to test the quality of PCBA?
The quality of PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) is tested through a series of rigorous procedures. These include visual inspections to identify defects like soldering issues or component misalignment, automated optical inspection (AOI) for precise inspection of solder joints and component placement, in-circuit testing (ICT) to check the electrical connectivity and functionality of specific components, functional testing to verify the overall operation of the assembly, and sometimes, thermal and environmental testing to ensure the PCBA can withstand various conditions. These tests collectively help ensure that the PCBA meets the desired quality standards and functions reliably in its intended application.
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) can be packaged using various methods, each with unique characteristics:
1. Bulk Packaging: Components are supplied in loose form and are manually placed on the PCB. It is cost-effective but can be labor-intensive and may require more handling.
2. Tape and Reel: Components are presented on carrier tapes, suitable for automated pick-and-place machines. This method is efficient for high-volume production and minimizes manual handling.
3. Tray Packaging: Components are held in trays or pockets, providing good protection for larger or delicate parts. However, it may require more storage space and manual handling.
4. Tube Packaging: Components are enclosed in plastic or anti-static tubes, safeguarding against ESD and physical damage during transportation, making it suitable for sensitive components.
Ensuring the production quality of PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) involves a comprehensive approach. This includes using high-quality components, maintaining strict adherence to assembly procedures, conducting regular quality inspections at various stages of production, employing skilled and trained personnel, and implementing robust quality control processes. Additionally, automated testing methods, such as in-circuit testing (ICT) and functional testing, help identify and rectify defects early in the production cycle. By following these practices and continuously monitoring and improving the manufacturing process, consistent and reliable PCBA quality can be achieved.
What are the common faults in the PCBA production process? How to deal with it?
Common faults in the PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) production process include soldering defects like solder bridges or cold joints, component misalignment, missing or wrong components, and solder paste stencil issues. To deal with these faults, it's essential to implement thorough quality control measures such as visual inspections, automated optical inspection (AOI), and in-circuit testing (ICT) to detect defects. Additionally, proper training of assembly operators and regular maintenance of equipment can help prevent these issues. When faults are identified, they should be addressed promptly through rework or repair processes to ensure the final product meets quality standards.
What is the life cycle of PCBA? Is maintenance required?
The life cycle of PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) can vary depending on its application, environmental factors, and component quality. In many cases, PCBA components have a typical operational life span of several years to a decade or more. Routine maintenance may not be required for the PCBA itself, but the end-product it is a part of may need maintenance or periodic upgrades. It's crucial to monitor and maintain the entire system to ensure reliable performance over its life cycle. However, in some high-reliability applications, PCBA components may be designed for extended life and undergo preventive maintenance to maximize their longevity.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICE
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.




