868 mhz pcb antenna design
With excellent project management skills, open communication, constant follow-up, and customer-centric values, we will make electronic development run smoothly. High-quality production is even harder to find. All our products comply with international quality standards and our customers come from different markets around the world. For example Uganda,Morocco,Greece,Algeria,Turks and Caicos Islands etc.
| Base Material | FR-4/CEM-1/CEM-3/Polyimild/PTFE/Rogers |
| Board Thickness | 0.3-4mm |
| Model Number | Custom PCB & PCB Assembly |
| Type | Aluminum PCB |
| Brand Name | FC |
| Copper Thickness | 0.2-2mil(9-51um) |
| Min. Hole Size | 0.1mm(4mil)for HDI / 0.15mm(6mil) |
| Min. Line Width | 0.075mm/0.075mm(3mil/3mil) |
| Min. Line Spacing | 0.003'' |
| Surface Finishing | HASL/OSP/Ag/ENIG/ENEPIG/Immersion silver/Tin |
| Board Size | Custom |
| Model Number | Customized |
| Base Material | FR4 Aluminum CEM-1 94V0 |
| Surface Finishing | HASLENIG OSP |
| Number of layer | 1-17layer |
| Other service | Components purchasing and assem |
| ly Solder mask | White Black Green Blue,Red,etc. |
| Dsign service | Available |
| Testing | Function testing |
| Certificate | RoHS, ISO/TS16949, ISO9001 |
| Name | High Quality led light aluminum pcb printed circuit board |
| Packaging Details | Vaccum package and standard carton outside High Quality led light aluminum pcb printed circuit board |
| Supply Ability | 43910 Square Meter/Square Meters per Month |
| Quantity (pieces) | > 26930 |
| Lead time (days) | 10 |
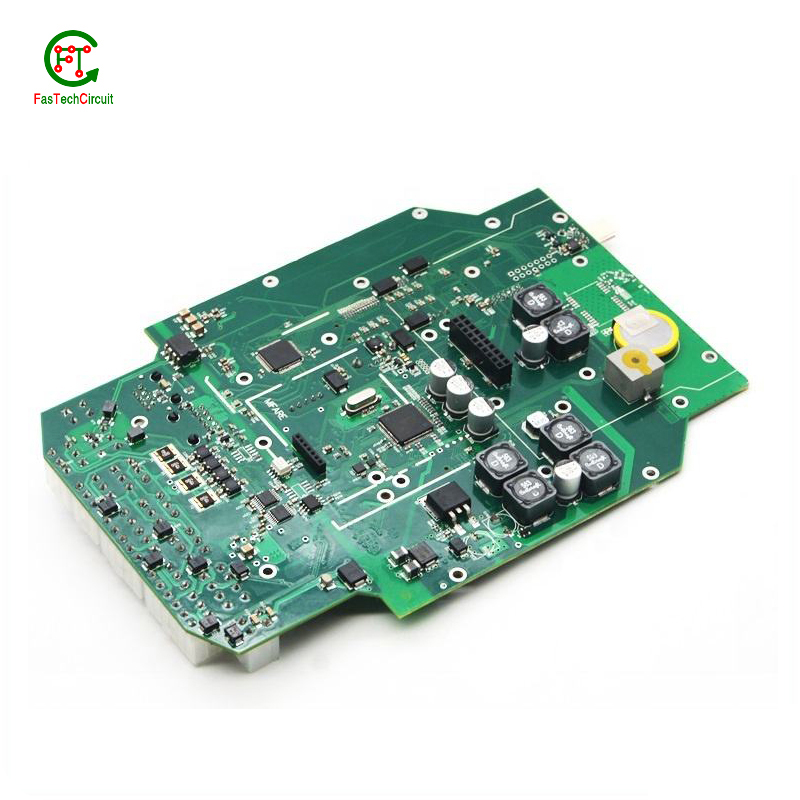

868 mhz pcb antenna design bearings FAQs Guide Welcome to our state-of-the-art PCB (Printed Circuit Board) products. We are proud to offer a comprehensive range of high-quality and versatile PCB solutions to meet the constantly evolving needs of the modern electronics industry.Our PCBs are expertly designed and manufactured using the latest technology and advanced techniques, ensuring reliability, durability, and exceptional performance for a wide range of applications. We understand the importance of precision and attention to detail in the production of PCBs and we are committed to meeting stringent quality standards.
2.How are 868 mhz pcb antenna designs tested for quality control?
3.What are the main components of a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
4.How are high-frequency signals handled on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
5.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used for high-speed data transmission?
6.What is the difference between single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
7.What is the difference between a copper pour and a trace on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
8.What techniques are used for reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
9.How are power and ground planes connected on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
10.What is embedded 868 mhz pcb antenna design technology?
11.What types of 868 mhz pcb antenna designs are there?
12.Can a 868 mhz pcb antenna design be used for both power and signal transmission?
13.What is a through-hole component?
14.What is the difference between a diode and a capacitor?
15.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used in automotive applications?
16.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used in high-frequency applications?
17.What is the difference between a gold-plated and a tin-plated 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
1.What is the minimum thickness of a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
We are committed to providing personalized solutions and established long -term strategic cooperative relationships with customers.
The minimum thickness of a PCB (printed circuit board) can vary depending on the materials and manufacturing processes used. However, the standard minimum thickness for a single-sided PCB is 0.6mm (0.024 inches) and for a double-sided PCB it is 0.8mm (0.032 inches). Thinner PCBs can be made, but they may be more fragile and have limitations on the components and circuitry that can be used.
2.How are 868 mhz pcb antenna designs tested for quality control?
We have broad development space in domestic and foreign markets. 868 mhz pcb antenna design have great advantages in terms of price, quality, and delivery date.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) testing is a critical step in the quality control process of electronic products. It ensures that all components and connections on the board are functioning correctly and that the PCB meets the required standards and specifications.
The testing process typically starts with a visual inspection to identify any visible defects, such as incorrect soldering or damaged components. Next, electrical testing is conducted to check the functionality of each individual component and the overall circuit.
One common method of testing is the use of a test fixture, which applies signals to the PCB and checks for correct responses. Other methods include automated optical inspection (AOI) and in-circuit testing (ICT).
Once the initial testing is completed, the PCB may undergo environmental testing to simulate real-life conditions and ensure its reliability and durability. This includes temperature and humidity cycling, vibration and shock testing, and more.
3.What are the main components of a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
We continuously upgrade our skills and knowledge to adapt to changing 868 mhz pcb antenna design market needs.
A typical PCB consists of several vital components, including a substrate material, copper traces, solder mask, silk screen, and plated through-holes. The substrate material acts as the base and provides mechanical support for the board. Copper traces, usually made of thin lines of copper foil, serve as the conductive paths for transmitting electrical signals. The solder mask, applied as a protective layer, prevents accidental short circuits and corrosion. Silk screen, a layer of ink-based labeling, aids in component identification. Lastly, plated through-holes enable electrical connection between different layers of the PCB board. These components work together to form a fully functioning PCB.
4.How are high-frequency signals handled on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
High-frequency signals are typically handled with great care and precision on a PCB to ensure optimal performance. This involves using high-quality materials, such as high-speed laminates and low-loss dielectrics, to minimize signal loss and interference. Additionally, designers must carefully consider the trace routing and placement of components on the PCB to minimize signal reflections and keep the signal path as short and direct as possible. Specialized techniques, like controlled impedance and shielding, may also be used to further improve signal integrity.
5.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used for high-speed data transmission?
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be used for high-speed data transmission. PCBs are commonly used in electronic devices and systems to connect and route electrical signals between components. They are designed to have specific trace widths, lengths, and impedance to ensure efficient and reliable transmission of high-speed signals. Additionally, PCBs can be designed with specialized materials and techniques, such as controlled impedance and differential signaling, to further optimize their performance for high-speed data transmission.
6.What is the difference between single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
We have established a good reputation and reliable partnerships within the 868 mhz pcb antenna design industry.
Single-sided PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a type of PCB that has components and traces on only one side of the board. The other side is usually used for soldering and mounting the board onto a larger circuit.
Double-sided PCB is a type of PCB that has components and traces on both sides of the board. The traces on both sides are connected through vias, which are small holes drilled through the board and plated with metal to create an electrical connection.
Multi-layer PCB is a type of PCB that has multiple layers of conductive material and insulating material sandwiched together. The layers are connected through vias, allowing for more complex and compact circuit designs. Multi-layer PCBs are used in more advanced and high-performance electronic devices.
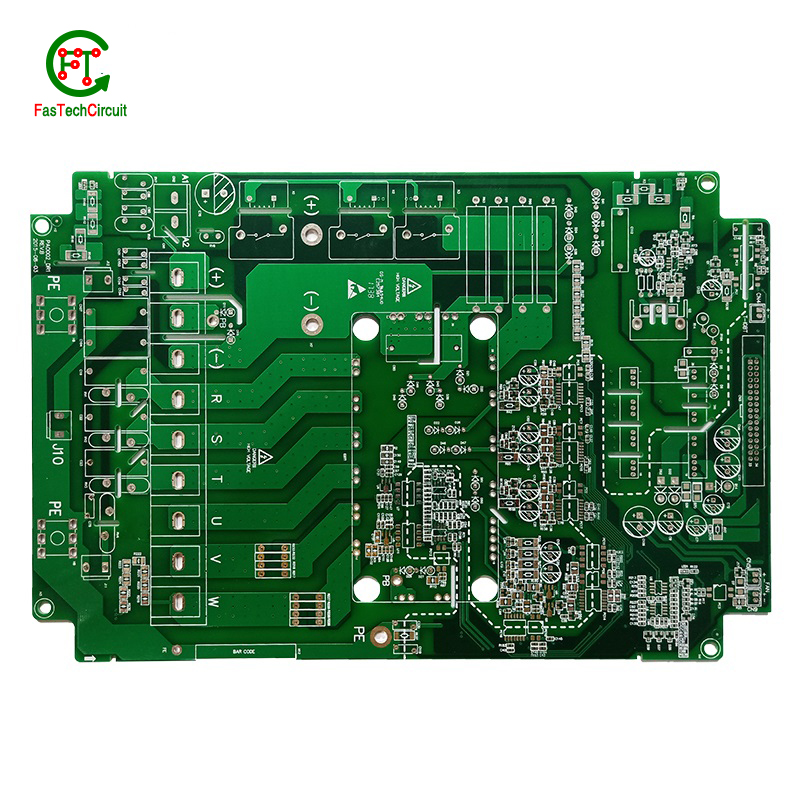
7.What is the difference between a copper pour and a trace on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
We adhere to the principle of quality first and have a complete production quality management system and quality inspection process.
A copper pour and a trace are two common electronic components that are found on a printed circuit board (PCB). A copper pour is a large area of copper that is used to connect multiple components or ground signals together on a PCB. This creates a solid and low resistance pathway for signals to flow. On the other hand, a trace is a thin line of copper used to connect individual components on a PCB. It carries a specific signal from one component to another. Unlike a copper pour, a trace can be designed to carry a specific current and have a specific width to meet the requirements of the circuit.
8.What techniques are used for reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a disturbance caused by electromagnetic radiation that can disrupt the proper functioning of electronic devices. To reduce EMI on a PCB, a number of techniques can be employed. One common technique is to use a ground plane, which acts as a shield to block electromagnetic waves from interfering with the circuit. Another approach is to use proper placement and routing of components and traces to minimize the length of signal paths and reduce the chances of signal crossover. Additionally, using components like capacitors and ferrite beads can help to filter out high-frequency noise. Careful consideration and design of the PCB layout is also crucial in reducing EMI, as the placement, size, and orientation of components can impact electromagnetic emissions. By employing these techniques, EMI on a PCB can be effectively reduced, leading to improved performance and reliability of electronic devices.
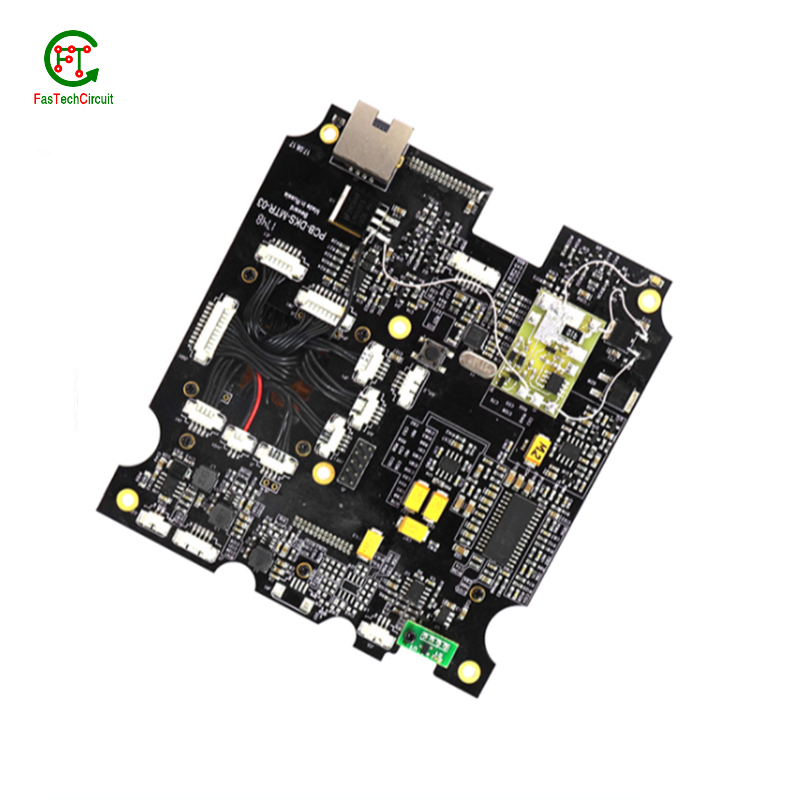
9.How are power and ground planes connected on a 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
Power and ground planes are typically connected on a PCB through vias, which are small holes drilled through the layers of the PCB. These vias are filled with conductive material, such as copper, and allow for the flow of current between the power and ground planes. The vias are strategically placed throughout the PCB to ensure a low impedance connection between the power and ground planes. Additionally, traces or copper pours can also be used to connect the power and ground planes on different layers of the PCB.
10.What is embedded 868 mhz pcb antenna design technology?
Our products & services cover a wide range of areas and meet the needs of different fields.
Embedded PCB technology refers to the integration of electronic components directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB) during the manufacturing process. This allows for a more compact and efficient design, as well as improved reliability and performance. The components are embedded within the layers of the PCB, rather than being mounted on the surface, resulting in a more streamlined and durable product. This technology is commonly used in applications such as smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronic devices.
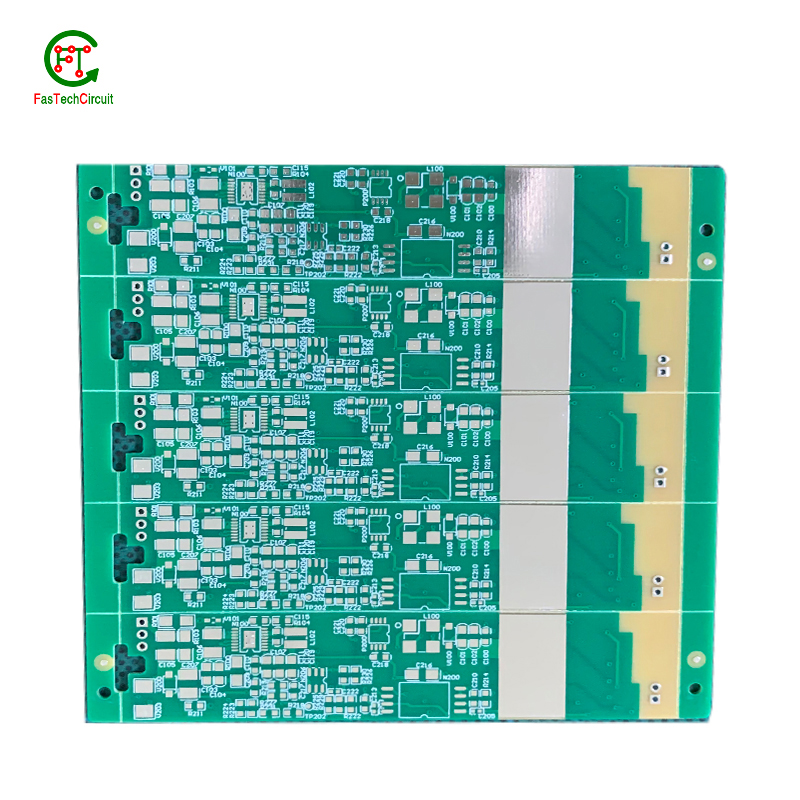
11.What types of 868 mhz pcb antenna designs are there?
As one of the 868 mhz pcb antenna design market leaders, we are known for innovation and reliability.
There are several types of PCBs, including single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, and flexible PCBs. Single-sided PCBs have components mounted on one side and conductive traces on the other. Double-sided PCBs have components mounted on both sides with conductive traces connecting them. Multi-layer PCBs have several layers of conductive traces and insulating material sandwiched together. Flexible PCBs are made from a flexible plastic material, allowing them to bend and twist for use in applications where traditional rigid PCBs are not suitable. Each type of PCB serves a different purpose and can be used in a variety of electronic devices and applications.
12.Can a 868 mhz pcb antenna design be used for both power and signal transmission?
Yes, a PCB (printed circuit board) can be used for both power and signal transmission. This is commonly seen in electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices. The PCB acts as a platform for connecting various components and circuits, including power sources and signal pathways. The power and signal traces on the PCB are designed to handle different levels of current and voltage to ensure efficient transmission and prevent interference between the two. However, it is important to properly design and layout the PCB to ensure proper separation and isolation of power and signal traces to avoid any potential issues.

13.What is a through-hole component?
We focus on providing high 868 mhz pcb antenna design quality products and services.
A through-hole component is an electronic component that has leads or pins that are inserted into holes on a printed circuit board (PCB) and then soldered to the opposite side of the board. This type of component is typically larger and more robust than surface mount components, and is often used for high-power or high-voltage applications. Through-hole components are also easier to replace or repair compared to surface mount components.
14.What is the difference between a diode and a capacitor?
We have a first -class management team, and we pay attention to teamwork to achieve common goals.
A diode is an electronic component that allows current to flow in only one direction. It has two terminals, an anode and a cathode, and works by allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode, but not in the reverse direction.
A capacitor, on the other hand, is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It has two conductive plates separated by an insulating material, and when a voltage is applied, one plate accumulates a positive charge and the other accumulates a negative charge. This allows the capacitor to store energy and release it when needed.
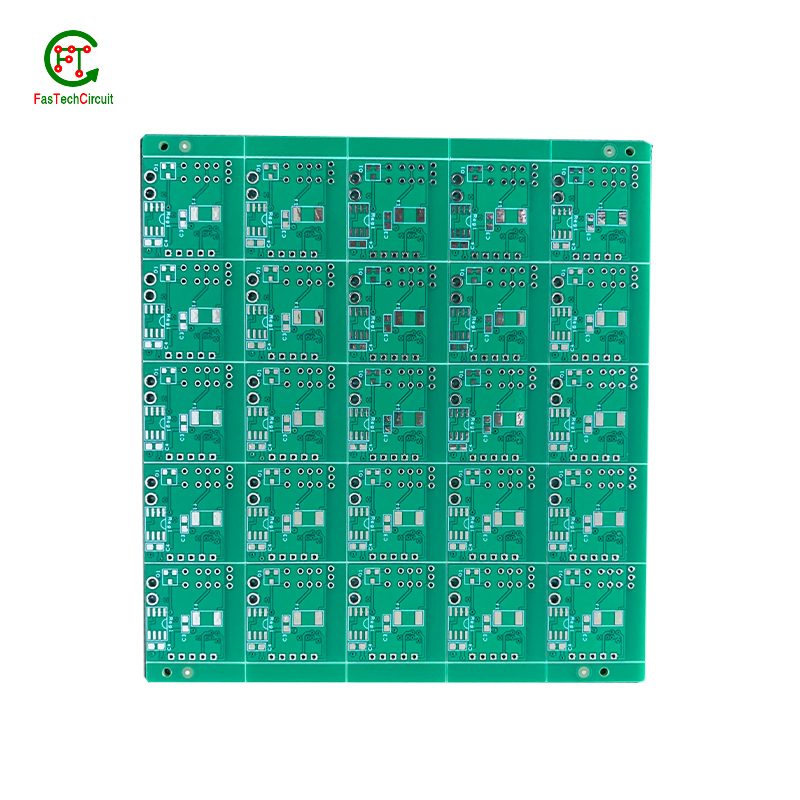
15.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used in automotive applications?
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be used in automotive applications. They are commonly used in various electronic systems in vehicles, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety systems. PCBs offer a compact and reliable way to connect and control electronic components in vehicles. They are also designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and moisture, making them suitable for use in automotive applications.
16.Can 868 mhz pcb antenna designs be used in high-frequency applications?
Our mission is to provide customers with the best solutions for 868 mhz pcb antenna design.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be used in high-frequency applications. However, the design and construction of the PCB must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance at high frequencies. This includes using specialized materials, such as high-frequency laminates, and implementing proper grounding and shielding techniques. Additionally, the layout and routing of the PCB must be optimized to minimize signal loss and interference.

17.What is the difference between a gold-plated and a tin-plated 868 mhz pcb antenna design?
A gold-plated PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a type of PCB that has a thin layer of gold coating on its surface. This layer is added through a process called electroplating and is commonly used to protect the PCB components from corrosion and increase the conductivity. On the other hand, a tin-plated PCB has a layer of tin coating on its surface, which is also applied through electroplating. Unlike gold plating, tin plating is mainly used to prevent oxidization and improve solderability.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICE
pcb board manufacturing How To Contact US
PCB from 1 to 30 layers, HDI, Heavy Copper, Rigid-flex board with "pcb board manufacturing One-Stop" service.

